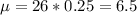Answer:
a)
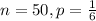
b)
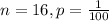
c)
Explanation:
Binomial probability distribution
The binomial probability is the probability of exactly x successes on n repeated trials, and X can only have two outcomes.
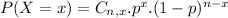
In which
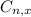 is the number of different combinatios of x objects from a set of n elements, given by the following formula.
is the number of different combinatios of x objects from a set of n elements, given by the following formula.
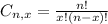
And
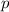 is the probability of X happening.
is the probability of X happening.
(a) A fair die is rolled 50 times. X = number of times a 5 is rolled
The die is rolled 50 times, so
 .
.
Each roll can have 6 outcomes. So the probability that 5 is rolled is
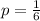
(b) A company puts a game card in each box of cereal and 1/100 of them are winners. You buy sixteen boxes of cereal, and X = number of times you win.
You buy 16 boxes of cereal, so
 .
.
1 of 100 are winners. So
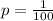 .
.
(c) Jack likes to play computer solitaire and wins about 25% of the time. X = number of games he wins out of his next 26 games.
He plays 26 games, so
 .
.
He wins 25% of the time, so
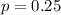
We have that
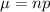 . So
. So