Answer:
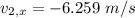
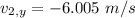
Solution:
As per the question:
Common terminal speed,
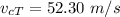
Mass of the one of the skydiver,
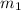 = 89.30 kg
= 89.30 kg
Velocity of the skydiver :
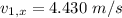
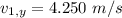
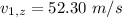
Mass of the other skydiver,
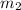 = 63.20 kg
= 63.20 kg
Now,
To calculate the components of velocity along X and Y axes:
Before getting separated, the momentum along X-axis is zero.
After the separation, the momentum along X-axis is zero.
Therefore,
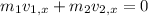
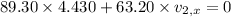
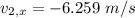
Now, consider the momentum along Y-axis:
Before separation, momentum = 0
After separation, momentum along Y-axis = 0
Therefore,
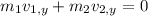
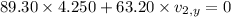
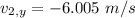
Thus the magnitude of the X and Y component of velocity are 6.259 m/s and 6.05 m/s respectively.