Answer:
a) 3.52
b) 0.002399
c) At α = .05 we reject the null hypothesis.
Explanation:
We are given the following information:
Population mean, μ = 6 μg per liter
Sample size, n = 12
Alpha, α = 0.05
6.94, 7.50, 5.87, 7.92, 8.66, 7.78, 7.95, 6.35, 6.16, 6.28, 5.68, 7.02
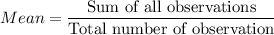
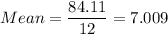
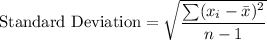
where
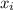 are data points,
are data points,
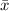 is the mean and n is the number of observations.
is the mean and n is the number of observations.
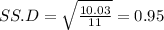
First, we design the null and the alternate hypothesis
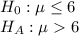
We use One-tailed t test to perform this hypothesis.
a) Formula:
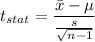
Putting all the values, we have
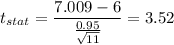
b) P-value for one tailed t-test at 11 degree of freedom and α = 0.05 is 0.002399
c) Since P-value < 0.05
The result is insignificant.
Thus, at α = .05 we reject the null hypothesis.