Answer:
18.5 ns.
Step-by-step explanation:
In order to develop the problem we must first identify the capacitance that is found
on the oscilloscope, like this:
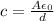
Where A scope of the oscilloscope,
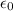 is Vacuum permittivity
is Vacuum permittivity
d = distance between the ones.
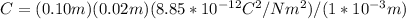
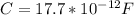
Defining the following variables in question we have to
Resistance (R) = 1000 Ohm
Meanwhile the Maximum Voltage (V_ {max}) applied is 100V
However, the maximum time to reach the voltage of 65V is
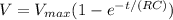
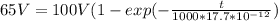
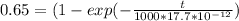
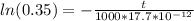
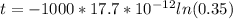
t = 18.5ns