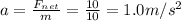Answer:
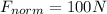
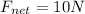
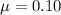
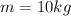
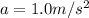
Step-by-step explanation:
To determine the normal force, we just need to analyze the situation along the vertical direction.
The box along the vertical direction is in equilibrium, so the equation of the forces is
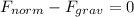
which means that
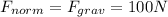
The net force can be determined by looking at the situation along the horizontal direction (since the net force in the vertical direction) is zero. Here we have:
- An applied force of 20 N forward,
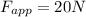
- A frictional force of 10 N backward,
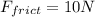
So, the net force is
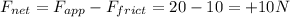 in the forward direction
in the forward direction
The expression for the frictional force is
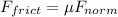
where
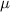 is the coefficient of friction. Solving for
is the coefficient of friction. Solving for
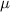 ,
,
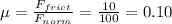
The force of gravity is given by
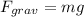
where m is the mass of the object and
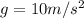 . Solving for m, we find the mass of the object:
. Solving for m, we find the mass of the object:
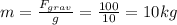
Finally, the acceleration can be found by using Newton's second law
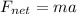
where a is the acceleration. Solving for a,