Answer:
91.1835 nm
Step-by-step explanation:
Given that the ionization energy of the oxygen molecule = 1314 kJ/mol
It means that
1 mole of oxygen molecules can be ionized by the energy = 1314 kJ = 1314000 J
1 mole of molecules contains 6.022 × 10²³ atoms
So,
6.022 × 10²³ atoms of oxygen molecules can be ionized by the energy = 1314000 J
1 atom require
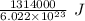 of energy
of energy
Energy =
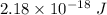
Also
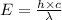
Where,
h is Plank's constant having value
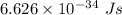
c is the speed of light having value
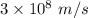
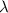 is the wavelength
is the wavelength
So,
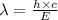
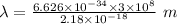
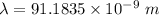
Also,
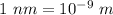
So, wavelength = 91.1835 nm