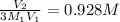Answer:
0.928 M
Step-by-step explanation:
The concentration of acid can be determined by using the volume used and the concentration and volume used of base.
We will use the law of equivalence of moles.
M₁V₁=M₂V₂
M₁ = concentration of base used
V₁ = volume of base used
M₂ = concentration of acid used =? (to be determined)
V₂ = volume of acid used
The initial concentration of KOH used is diluted so let us find the final concentration of KOH after dilution
initial moles = final moles
initial concentration X initial volume = final concentration X final volume
6.2 X 2.1 = 250 X final concentration
final concentration = 0.052 M = M₁
V₁ = 36.9 mL
V₂ = 6.2 mL
Here with each mole of phosphoric acid three moles of KOH are used.
Therefore
3 M₁V₁ = M₂V₂
M₂ =