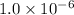Answer : The value of
 for the equilibrium is
for the equilibrium is
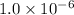
Explanation : Given,
Total pressure = 0.200 atm
The balanced equilibrium reaction is,
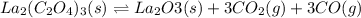
First we have to calculate the partial pressure of
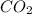 and
and
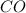 .
.
From the balanced reaction we conclude that,
The moles of
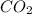 is equal to the moles of
is equal to the moles of
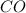 . So,
. So,
Total number of moles = 2
Partial pressure of
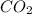 =
=
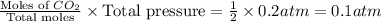
and,
Partial pressure of
 =
=
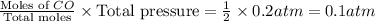
Now we have to calculate the value of equilibrium constant.
The expression of equilibrium constant
 for the reaction will be:
for the reaction will be:
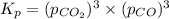
Now put all the values in this expression, we get :
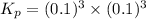
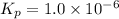
Therefore, the value of
 for the equilibrium is
for the equilibrium is