Answer
given,
mass of the cat = 8 kg
length of the ramp = 2 m
inclined at = 19°
force exerted = 60 N
cat is moving at speed = 2 m/s
velocity when it reaches at the top = ?
using work energy theorem
work done by the gravity = - mgL sin θ
total work (w)
= F x - mgL sin θ
= 60 x 2 - 8 x 9.8 x 2 sin 19°
= 68.95 J
initial kinetic energy
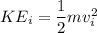
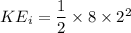
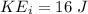
change in kinetic energy is work done
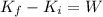
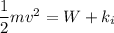
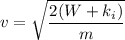
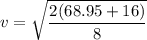
v = 4.61 m/s