Answer:
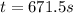 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
The heat needed will be provided by the power dissipated by the resistor. This power gives certain energy per unit time, so we multiply it by time to get the energy provided:
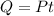 .
.
The equation of heat given mass, specific heat and temperature change is
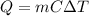 , and the equation of power dissipated by a resistor is
, and the equation of power dissipated by a resistor is
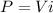 .
.
Putting all together:
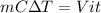 .
.
Which means:
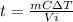 .
.
From 23.0°C to 100°C we have a
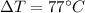 , which we won't need to put in Kelvin in this case since it is a variation, so for our values we have:
, which we won't need to put in Kelvin in this case since it is a variation, so for our values we have:
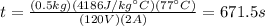 .
.