Answer:
pH = 9.6
Step-by-step explanation:
According to Brönsted-Lowry theory, NH₃ is a base and NH₄⁺ its conjugate acid. When they are together in a solution, the form a buffer, which is used to resist abrupt changes in pH when an acid or a base is added. pOH fro a buffer can be found using Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
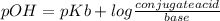
Since NH₄Cl is a strong electrolyte, [NH₄Cl] = [NH₄⁺]
![pOH = pKb + log([NH_(4)^(+) ])/([NH_(3)]) =4.7+log(0.035M)/(0.070M) =4.4](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/p9wdye95proep9vtypcg2igqaijcghuv4e.png)
Now, we can find pH using the following expression:
pH + pOH = 14
pH = 14 - pOH = 14 - 4.4 = 9.6