Step-by-step explanation:
The given data is as follows.
Specific heat of water =
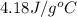
Heat of fusion of water = 334 J/g
Mass of water = 200 g
On bringing water at
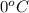 , heat released will be as follows.
, heat released will be as follows.
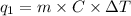
=
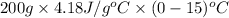
= -12540 J
or, = -12.540 kJ (as 1 kJ = 1000 J)
Now, calculate the heat releasedwhen water freezes at
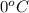 as follows.
as follows.
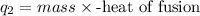
=
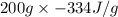
= -66800 J
or, = -66.80 kJ
Therefore, total heat released in freezing water will be as follows.
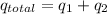
= (-12.540 - 66.80) kJ
= -79.34 kJ
Hence,
amount of heat released in freezing water = heat used to vaporize
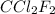
Now, heat of vaporization of
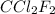 = 289 J/g
= 289 J/g
Total heat released in freezing water = -79.34 kJ
Heat consumed to vaporize
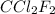 = 79.34 kJ = -79340 J
= 79.34 kJ = -79340 J
Therefore, calculate the mass of
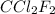 vaporized as follows.
vaporized as follows.
Mass of
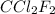 vaporized =
vaporized =
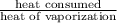
=
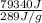
= 274.53 g
Thus, we can conclude that 274.53 g mass of this substance must evaporate to freeze 200 g of water initially at
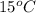 .
.