Answer:
ΔH = -55.73 kJ/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
Since the density of water is 1 g/ml and the problem wants us to use this value to find the mass of NaOH and HNO3 we arrange the original equation of
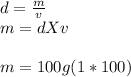
Since no heat was lost or gained
qrxn+qsoln=0. ----> qrxn=-qsoln.
qsol = mc*(
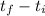 )
)
The mass of the solution is the mass of NaOh and HNO3. 100+100= 200.
You plug in the remaining numbers using 4.18 as the heat capacity and 2 as the change in temperature:
qsol=200*(4.18)*(2)= 1672 J
qrxn= -1672 J
Now ΔH = qrxn over the amount in moles or grams. This problem asks for NaOH in moles. To calculate this we use the concentration formula
M=
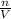 . -----> n=V*M.
. -----> n=V*M.
Note that you must convert 100 ml to L to use this equation. So we have
n=0.1*0.300 where n=0.03
ΔH =
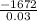
ΔH = -55733.3 J/mol
ΔH = -55.73 kJ/mol