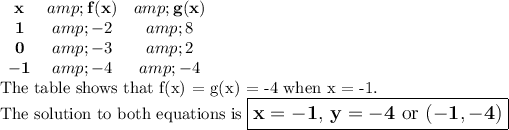Answer:
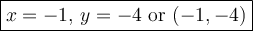
Explanation:
ƒ(x):
-x + y = -3
For easier calculations, add x to each side. Then
y = -3 + x
x = 1: y = -3 + 1 = -2
x = 0: y = -3 + 0 = -3
x = -1: y = -3 + (-1) = -3 - 1 = -4
g(x):
-6x + y = 2
y = 2 + 6x
x = 1: y = 2 + 6(1) = 8
x = 0: y = 2 + 0(1) = 2
x = -1: y = 2 + 6(-1) = 2 - 6 = -4