Answer:
Reagent A =
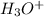
Reagent B=
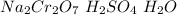
Intermediate C= δ-Valerolactone
Step-by-step explanation:
In the reaction from the alkene to the alcohol, we can use the alkene hydration in which the hydronium ion is added to the double bond followed by the attack of water to produce the alcohol.
Then in the conversion from alcohol to ketone can be produced if an oxidant reactive is used. In this case the Jones reagent (
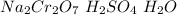 ).
).
The intermediate is a structure produced by a peroxyacid. This reaction would introduce an ester group in the cycle generating the δ-Valerolactone (Figure 1).