Answer:
When water is surrounding T_s = 34.17 degree C
When air surrounding T_S = 1434.7 degree C
from above calculation we can conclude that air is less effective than water as heat transfer agent
Step-by-step explanation:
Given data:
length = 300 mm
Outer diameter = 30 mm
Dissipated energy = 2 kw = 2000 w
Heat transfer coefficient IN WATER = 5000 W/m^2 K
Heat transfer coefficient in air = 50 W/m^2 K
we know that
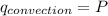
From newton law of coding we have
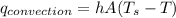
 is surface temp.
is surface temp.
T - temperature at surrounding
/(\pi hDL) = (T_s - T_(\infity))](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/3qzq8p6zpxtabdbfyrutb0795raa0e3256.png)
solving for[/tex] T_s [/tex] w have
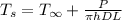
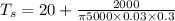
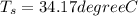
When air is surrounding we have
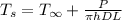
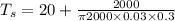
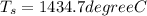
from above calculation we can conclude that air is less effective than water as heat transfer agent