Answer:
For the interval [1, 1.0] the average velocity is
![(\Delta h)/(\Delta t)={Undefined}]()
For the interval [1, 1.01] the average velocity is
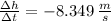
For the interval [1, 1.005] the average velocity is
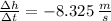
For the interval [1, 1.001] the average velocity is
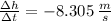
The instantaneous velocity at t = 1 is
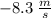 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
The average velocity over
![[t_0,t_1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/physics/college/4rr2dn2e6ip6mzf325dps1zef760wm62o3.png) is
is
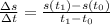
where
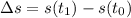 = change in position
= change in position
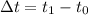 = change in time (length of interval)
= change in time (length of interval)
We know that the height in meters a t seconds is given
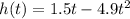
so the average velocity is
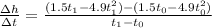
Consider the interval [1, 1.0]
![(\Delta h)/(\Delta t) = ((1.5(1.0) - 4.9(1.0)^2)-(1.5(1) - 4.9(1)^2))/(1.0-1)\\\\(\Delta h)/(\Delta t) =\{Undefined}]()
For the interval [1, 1.01]
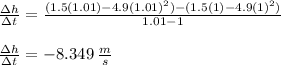
For the interval [1, 1.005]
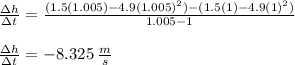
For the interval [1, 1.001]
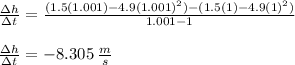
The instantaneous rate of change is the limit of the average rates of change. We estimate the instantaneous rate of change at
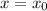 by computing the average rate of change over smaller and smaller intervals
by computing the average rate of change over smaller and smaller intervals
From the calculations above we can see when the time interval shrinks the average velocity tends to the value
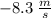 . This suggests that this value is a good candidate for the instantaneous velocity at t = 1.
. This suggests that this value is a good candidate for the instantaneous velocity at t = 1.