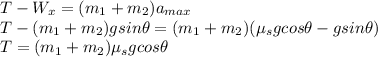Answer:
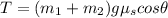
Step-by-step explanation:
Using the free body diagram of the load, we obtain according to Newton's laws:
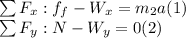
In this case we have:
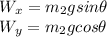
We have to know the load maximum acceleration in order to calculate the maximum tension. So, we replace
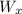 and
and
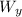 in (1) and (2):
in (1) and (2):
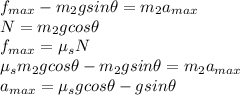
Now, we use the free body diagram of both bodies. Thus, we have: