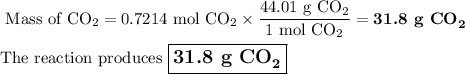Answer:
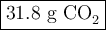
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given the masses of two reactants and asked to determine the mass of the product.
This looks like a limiting reactant problem.
1. Assemble the information
We will need a balanced equation with masses and molar masses, so let’s gather all the information in one place.
MM: 114.23 32.00 44.01
2C₈H₁₈ + 25O₂ ⟶ 16CO₂ + 18H₂O
Mass/g: 10.3 69.
2. Calculate the moles of each reactant
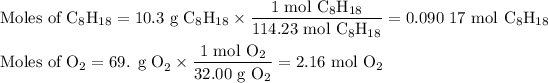
3. Calculate the moles of CO₂ from each reactant
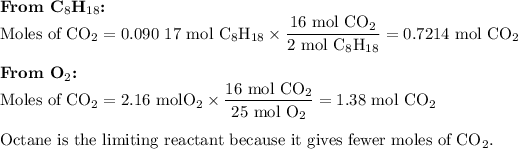
4. Calculate the mass of CO₂