Answer: b.
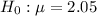 vs
vs
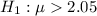
Explanation:
Let
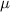 be the population mean.
be the population mean.
Given : The number of entrees purchased in a single order at a Noodles & Company restaurant has had an historical average of 2.05 entrees per order.
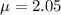
Claim : The average number of entrees per order was greater than expected.
i.e.
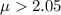
Hence, the correct null and alternative hypotheses for the given description:-
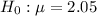
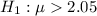 [Alternative hypothesis shows significance difference.]
[Alternative hypothesis shows significance difference.]
Since , the alternative hypothesis is right-tailed , so the test is a right tailed test.
Test statistic :
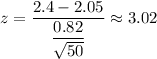
p-value : P(z>3.02)=0.0012639
Since p-value (0.0012639) is less than the significance level (0.05) , so we reject the null hypothesis.
Conclusion : The average number of entrees per order was greater than expected