Answer:
2 M
General Formulas and Concepts:
Math
Pre-Algebra
Order of Operations: BPEMDAS
- Brackets
- Parenthesis
- Exponents
- Multiplication
- Division
- Addition
- Subtraction
Chemistry
Unit 0
- Reading a Periodic Table
- Using Dimensional Analysis
Aqueous Solutions
- Molarity = moles of solute / liters of solution
Step-by-step explanation:
Step 1: Define
36.7 g CaF₂
300 mL H₂O
Step 2: Identify Conversions
Molar Mass of Ca - 40.08 g/mol
Molar Mass of F - 19.00 g/mol
Molar Mass of CaF₂ - 40.08 + 2(19.00) = 78.08 g/mol
1000 mL = 1 L
Step 3: Convert
Solute
- Set up:
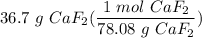
- Multiply:
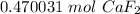
Solution
- Set up:
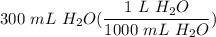
- Multiply:
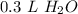
Step 4: Find Molarity
- Substitute [M]:
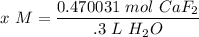
- Divide:
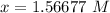
Step 5: Check
Follow sig fig rules and round. We are given 1 sig fig as our lowest.
1.56677 M ≈ 2 M