Answer:
Remember,
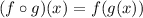 and the range of g must be in the domain of f.
and the range of g must be in the domain of f.
a)
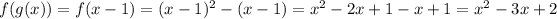
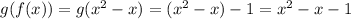
The domain of f(g(x)) and g(f(x)) is the set of reals.
b)
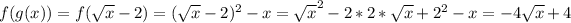
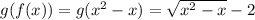
The domain of f(g(x)) is the set of nonnegative reals and the domain of g(f(x)) is the set of number such that
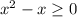
c)
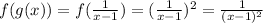
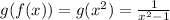
The domain of f(g(x)) is the set of reals except the 1 and the domain of g(f(x)) is the set of reals except the 1 and -1
d)
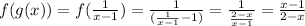
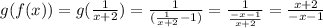
The domain of f(g(x)) is the set of reals except 2, and the domain of g(f(x)) is the set of reals except -1.
e)
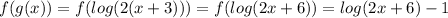
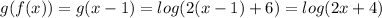
The domain of f(g(x)) is the set of nonnegative reals except -3. The domain of g(f(x)) is the set of nonnegative reals except -2.