Answer:
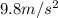
Step-by-step explanation:
First of all, we analyze the vertical direction.
Along this direction, the object is in equilibrium, so its acceleration is zero, and therefore the net force on it is zero. There are only two forces acting on the object vertically: the weight, W (downward), and the normal force, N (upward), and since the net force must be zero, we can write
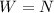
And since N = 60 N, the weight of the object is
W = 60 N
From this, we can also find the mass of the object, using the equation:
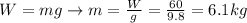
where
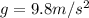 is the acceleration of gravity.
is the acceleration of gravity.
Now we analyze the forces along the horizontal direction. We have:
A pulling force of F=100 N forward
A frictional resistance of
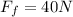 backward
backward
So the equation of motion in this direction is
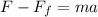
And solving for a, we find the acceleration of the object:
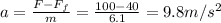
in the horizontal direction, forward.