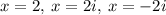Answer:
(a) The solutions are:
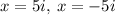
(b) The solutions are:
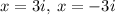
(c) The solutions are:
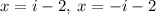
(d) The solutions are:
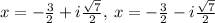
(e) The solutions are:
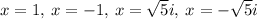
(f) The solutions are:
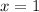
(g) The solutions are:
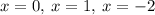
(h) The solutions are:
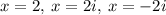
Explanation:
To find the solutions of these quadratic equations you must:
(a) For
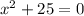
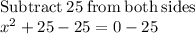
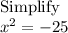
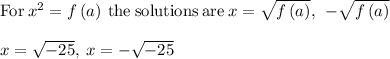
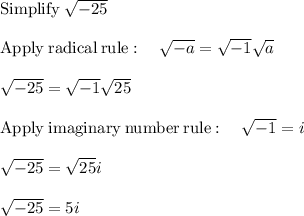
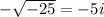
The solutions are:
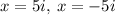
(b) For
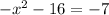
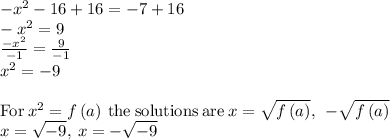
The solutions are:
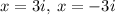
(c) For
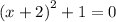
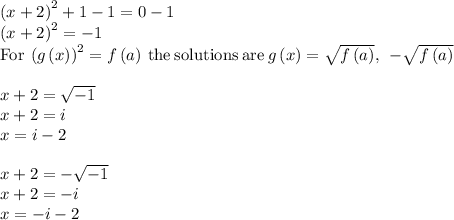
The solutions are:
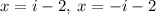
(d) For
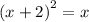
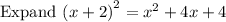
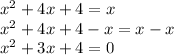
For a quadratic equation of the form
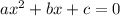 the solutions are:
the solutions are:
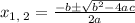
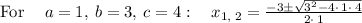

The solutions are:
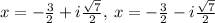
(e) For
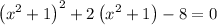
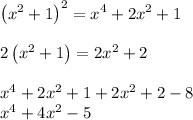
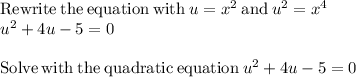
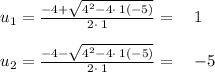
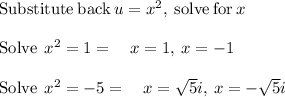
The solutions are:
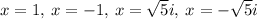
(f) For
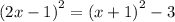
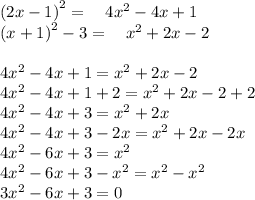
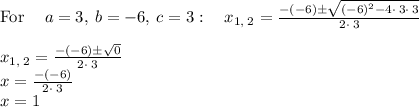
The solutions are:
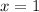
(g) For
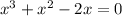
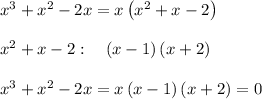
Using the Zero Factor Theorem: = 0 if and only if = 0 or = 0
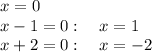
The solutions are:
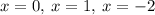
(h) For
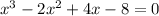
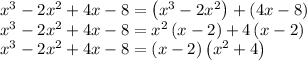
Using the Zero Factor Theorem: = 0 if and only if = 0 or = 0
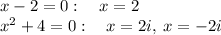
The solutions are: