Answer:
82.32 J
Step-by-step explanation:
Given:
Mass,
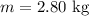
Initial height,
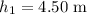
Final height,
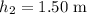
As the mass is dropped, its initial velocity is 0 m/s.
So, initial kinetic energy is also 0 J.
Now, according to conservation of energy,
Increase in Kinetic energy is equal to the decrease in potential energy.
Here, Decrease in potential energy is given as,
Δ
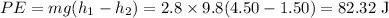
Now, increase in kinetic energy is equal to the kinetic energy at height
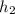 as the initial kinetic is 0.
as the initial kinetic is 0.
∴ Kinetic energy at height 1.50 m above ground is given as the decrease in potential energy.
So, Kinetic energy = Decrease in potential energy =
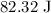
Kinetic energy at height 1.50 m above ground is
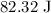 .
.