Answer:
the emprical formula is C4H3O2
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the empirical formula we should estimate the amount of each atom present.
It was generated CO2 and H2O, so we can estimate the moles of C, H and O in the sample.
1. moles of C can be estimated from CO2 generated
- First calculate the moles of CO2 from the mass generated of CO2 (1.471) using the molecular weight. MwCO2= 12.01+2*16 = 44.01 g/mol, so the moles of CO2 are
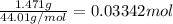
- Note that each CO2 has 1 C so moles of C= 0.03342
2. moles of H can be estimated from H2O generated
- First calculate the moles of H2O using mass generated (0.226g) and molecular weight. MwH2O= 2*1.008+16 = 18.016 g/mol, so the moles of H2O are
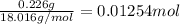
- Note that each H2O has 2 H so moles of H= 2*0.01254 =0.02509
3. O can not be calculated in the same way, since the combustion of the sample uses oxygen from air, so the oxygen in the products is not all from the sample. We calculate it from initial sample mass and the mass of C and H.
- Mass of C and O is calculated multiplyng the moles by the molecular weight. Mass of C = 0.03342*12.01= 0.4014g and Mass of H =0.02509*1.008= 0.02509g
- Mass of O = mass sample - mass C - mass H = 0.6943 - 0.4014 - 0.02509 = 0.26781g
- Moles of O =
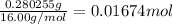
4. Now we can estimate the mole ratio C:H:O
C:H:O
0.03342:0.02509:0.01674
In order to obtain integer we should divide by the minor number and
1.9964:1.4988:1 rounding... 2:1.5:1
We have decimals yet. Multiply all by the smallest integer needed to get all integer numbers, in this case 2
2*(2:1.5:1)=4:3:2
So the emprical formula is C4H3O2