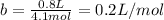Answer:
The fraction of the volume in a container actually occupied by Ar atoms is a) 6.1L/mol and b) 0.2L/mol
Step-by-step explanation:
The constant b is equal to four times the total volume actually occupied by the molecules of a mole of gas thus,
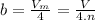 (1)
(1)
where Vm is the molar volume, V is the volume and n is the number of moles.
Also, for an ideal gas the equation of gases is P.V = n.R.T (2)
where P is the pressure, V is the volume, n is the number of moles, R is the gases constant and T is the temperature.
In a) the STP conditions establishes pressure (P) of 1 atm and a temperature (T) of 298K. Using the equation (2) the volume of 1 mol of argon is 24.4L, thus
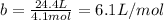
In b) at 100 atm pressure and 0 degrees Celsius (or 273K) using the equation (2) the volume of 1 mol of argon is 0.2L, thus