Answer: 5.85kJ/Kmol.
Step-by-step explanation:
The balanced equilibrium reaction is
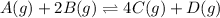
The expression for equilibrium reaction will be,
![K_p=\frac{[p_(D)]* [p_(C)]}^4{[p_(B)]^2* [p_(A)]}](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/high-school/hhtib0icbxw6ws2qpznodf8o4rbk21y4pi.png)
Now put all the given values in this expression, we get the concentration of methane.
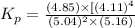
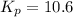
Relation of standard change in Gibbs free energy and equilibrium constant is given by:
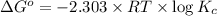
where,
R = universal gas constant = 8.314 J/K/mole
T = temperature =
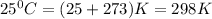
 = equilibrium constant = 10.6
= equilibrium constant = 10.6
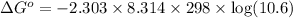
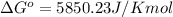
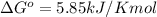
Thus standard change in Gibbs free energy of this reaction is 5.85kJ/Kmol.