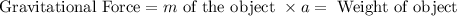The magnitude of the gravitational force acting on an object is weight of the object.
Answer: Option B
Explanation:
Any kind of force is a vector quantity having magnitude and direction. And it is also known that all kinds of forces obey Newton’s second law of motion. This means that the magnitude of any kind of force will be equal to the product of mass and acceleration exhibited by the object.
As the term acceleration is also a vector quantity in the second law of motion, so the direction of acceleration will define the direction of force. Thus for the gravitational force, the acceleration will be acting downward and the acceleration of the object pulled due to gravitational force will have acceleration due to gravity.
So the Newton’s second law of motion representation of gravitational force will be
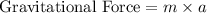
Now this product is also equal to the weight of the object as weight of any object is defined as the mass of the object influenced by gravitational pull. So,