Answer:
(a) Oxidation: Fe(II)(cyt b) ⇌ Fe(III)(cyt b) + e⁻
Reduction: Fe(III)(cyt c1) + e⁻ ⇌ Fe(II)(cyt c1)
(b) K = 750; spontaneous
Step-by-step explanation:
(a) Half-reactions
Oxidation: Fe(II)(cyt b) ⇌ Fe(III)(cyt b) + e⁻
Reduction: Fe(III)(cyt c1) + e⁻ ⇌ Fe(II)(cyt c1)
Overall: Fe(II)(cyt b) + Fe(III)(cyt c1) ⇌ Fe(III)(cyt b) + Fe(II)(cyt c1)
(b) Equilibrium constant
(i) Standard cell potential
The standard reduction potentials are
E°/V
Fe(III)(cyt c1) + e⁻ ⇌ Fe(II)(cyt c1); 0.25
Fe(III)(cyt b) + e- ⇌ Fe(II)(cyt b); 0.08
For the reaction in Part (a),
E°/V
Fe(II)(cyt b) ⇌ Fe(III)(cyt b) -0.08
Fe(III)(cyt c1) ⇌ Fe(II)(cyt c1) 0.25
Fe(II)(cyt b) + Fe(III)(cyt c1) ⇌ Fe(III)(cyt b) + Fe(II)(cyt c1) 0.17
The standard cell potential is 0.17 V.
(ii) Equilibrium constant
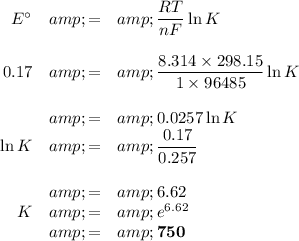
E° and K are positive, so the reaction is spontaneous.