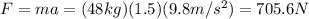Answer:
a)
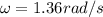
b)
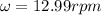
c)
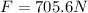
Step-by-step explanation:
a) The angular velocity is related to the centripetal acceleration by the formula
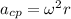 , which for our purposes we will write as:
, which for our purposes we will write as:
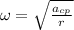
Since we want this acceleration to be 1.5 times that due to gravity, for our values we will have:
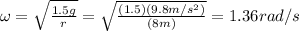
b) 1 rpm (revolution per minute) is equivalent to an angle of
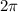 radians in 60 seconds:
radians in 60 seconds:
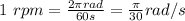
Which means we can use the conversion factor:
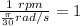
So we have (multiplying by the conversion factor, which is 1, not affecting anything but transforming our units):
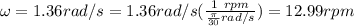
c) The centripetal force will be given by Newton's 2nd Law F=ma, so on the centripetal direction for our values we have: