Answer:
block K = 29.39 J and spring #1 Ke = 360 J
Step-by-step explanation:
In this problem we have that the elastic energy of the spring becomes part kinetic energy and the part in work against the force of friction, so, to use the law of conservation of energy, the decrease in energy is the rubbing force work
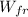 = Ef - E₀
= Ef - E₀
Let's look for the energies
Initial
E₀ = Ke = ½ k₁ x₁²
Final, this is just before starting to compress the spring
Ef = Ke = ½ m v²
The work of the rubbing force is
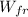 = -fr x
= -fr x
Let's write Newton's second law the y axis
N-W = 0
N = W
fr = μ N
fr = μ mg
Let's replace
-μ mg x = ½ m v² - ½ k₁ x₁²
v² = 2/m (½ k₁ x1₁² -μ mg x)
v² = 2/6 (½ 2000 0.6²2 - 0.5 6 9.8 1) = 1/3 (360 - 29.4)
v = 3.13 m / s
With this value we calculate the energy of the block
K = ½ m v²
K = ½ 6 3.13²
K = 29.39 J
Calculate eenrgy of the spring ke 1
Ke = ½ k₁ x₁²
Ke = ½ 2000 0.60²
Ke = 360 J