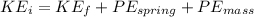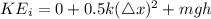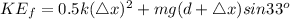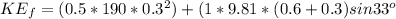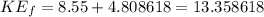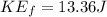Answer:
(a)
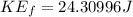
(b)
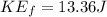
Step-by-step explanation:
(a)
Let compressed length be \triangle x
Initial distance, d= 0.6m
From the law of conservation of energy
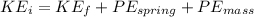 where
where
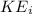 is the initial kinetic energy,
is the initial kinetic energy,
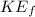 is final kinetic energy,
is final kinetic energy,
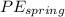 is potential energy of spring,
is potential energy of spring,
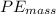 is potential energy of the block
is potential energy of the block
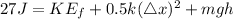 where m is mass, g is gravitational constant and h is height, k is spring constant=190
where m is mass, g is gravitational constant and h is height, k is spring constant=190
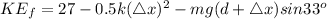
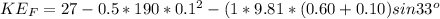
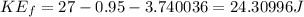
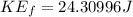
(b)
When at rest, the final velocity is zero
From the law of conservation of energy