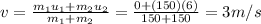Answer:
B. 3 m/s
Step-by-step explanation:
We can solve the problem by using the law of conservation of momentum; in fact, the total momentum before and after the collision must be conserved. So we can write:
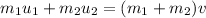
where:
m1 = 150 kg is the mass of spaceship 1
m2 = 150 kg is the mass of spaceship 2
u1 = 0 m/s is the initial velocity of spaceship 1
u2 = 6 m/s is the initial velocity of spaceship 2
v is the velocity of the two ships after they collide and stick together
Solving for v, we find: