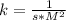Answer:
a)
![rate=r=k[NO]^(2) [Br_(2)]^(1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/5fgymcx66loyn48wicho5y0m9rx7lfoc2a.png)
b)
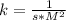
Step-by-step explanation:
First of all you need to indicate the reaction order of each reactant (
 and
and
 ):
):
1.
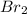
Note that if
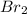 concentration (
concentration (
![[Br_(2) ]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/v7rs6z9jqgpm55zhcf3wi20ts49f6jtksa.png) ) is reduced to 1/3 of its initial value, the rate of the reaction is also reduced to 1/3 of its initial value, it means:
) is reduced to 1/3 of its initial value, the rate of the reaction is also reduced to 1/3 of its initial value, it means:
![[Br_(2) ]=1/3](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/eyw9uel7j8m7viksg4oijv56veyujredqp.png) then
then
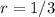
As the change in the rate of the reaction is equal to the change of the initial concentration of
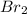 , you could concluded that the reaction is first order with respect to
, you could concluded that the reaction is first order with respect to
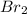
2.
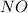
Now, note that if
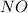 concentration (
concentration (
![[NO]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/2n3pvq040it0tve0k7qo6ka6ls9r6hu9v3.png) ) is multiplied by 3.69, the rate of the reaction increases by a factor of 13.6. In this case, to know the ratio could be advisable divide the rate of the reaction (13.6) over the factor whereby was multiplied the concentration (3.69), as follows:
) is multiplied by 3.69, the rate of the reaction increases by a factor of 13.6. In this case, to know the ratio could be advisable divide the rate of the reaction (13.6) over the factor whereby was multiplied the concentration (3.69), as follows:
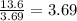
As the result is the same factor 3.69 you could concluded that the change of the rate of reaction is proportional to the square of the concentration of A:
![r=[NO]^(2) =3.68^(2) =13.6](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/u3mauswv31rn2ki28bvprlmn1542h6wc1r.png)
It means that the reaction is second order with respect to
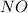
3. Rate Expression
Remember that the rate expression of the reactions depend on the concentration of each reactant and its order. In this case we have 2 reactants:
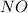 and
and
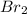 , then we have a rate law depending of 2 concentrations, as follows:
, then we have a rate law depending of 2 concentrations, as follows:
![rate=r=k[NO]^(2) [Br_(2)]^(1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/5fgymcx66loyn48wicho5y0m9rx7lfoc2a.png)
Note that the expression is the result of the concentration of each reactant raised to its reaction order (previously determined)
Note: I hope that you do not mix up the use of the rates of reaction of each reactant, that is experimentally determined, with the stoichiometric coefficient, are different.
4. Rate constant units (k)
Assuming concentration is expressed as
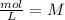 and time is in second, to find the units of k we need to solve an equation with units and with supporting of the rate equation previously obtained, as follows:
and time is in second, to find the units of k we need to solve an equation with units and with supporting of the rate equation previously obtained, as follows:
![r=k[NO]^(2) [Br_(2)]^(1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/rva03da13bxx1ixxhethrwkb9pwih6v907.png)
Where:
![[r]=[(M)/(s)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/oqz6fust5mp6o9aj3wvyfw0ddnhmz823fc.png)
![[[NO]]=[M]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/jdpfwreuds9z3bwwuga2oncqrrza5hs8d1.png)
![[ [Br_(2)]]=[M]](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/engineering/college/na4ma3r4ds13yrf51s9yi71nnekjc0wzwj.png)
Then:
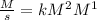
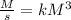
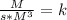
The units of the rate constant k are: