Answer: 2. Solution A attains a higher temperature.
Explanation: Specific heat simply means, that amount of heat which is when supplied to a unit mass of a substance will raise its temperature by 1°C.
In the given situation we have equal masses of two solutions A & B, out of which A has lower specific heat which means that a unit mass of solution A requires lesser energy to raise its temperature by 1°C than the solution B.
Since, the masses of both the solutions are same and equal heat is supplied to both, the proportional condition will follow.
We have a formula for such condition,
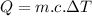 .....................................(1)
.....................................(1)
where:
 = temperature difference
= temperature difference
- c= specific heat of the body
Proving mathematically:
According to the given conditions
- we have equal masses of two solutions A & B, i.e.
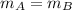
- equal heat is supplied to both the solutions, i.e.
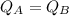
- specific heat of solution A,
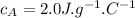
- specific heat of solution B,
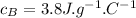
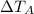 &
&
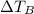 are the change in temperatures of the respective solutions.
are the change in temperatures of the respective solutions.
Now, putting the above values
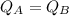
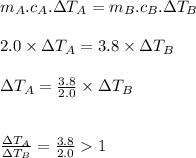
Which proves that solution A attains a higher temperature than solution B.