Answer:
a. Moles of
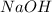 = 0.001643 moles
= 0.001643 moles
b. 0.296 g
c. 0.3098 g
d. Not acceptable
Step-by-step explanation:
a.
Considering:
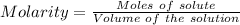
Or,
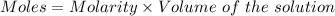
Given :
For
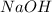 :
:
Molarity = 0.1052 M
Volume = 15.62 mL
The conversion of mL to L is shown below:
1 mL = 10⁻³ L
Thus, volume = 15.62×10⁻³ L
Thus, moles of
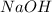 :
:
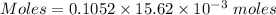
Moles of
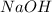 = 0.001643 moles
= 0.001643 moles
b.
The reaction of NaOH with the acetylsalicylic acid is in the ratio of 1:1.
Thus, Moles of NaOH = Moles of acetylsalicylic acid = 0.001643 moles
Molar mass of acetylsalicylic acid = 180.16 g/mol
The formula for the calculation of moles is shown below:
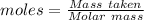
Thus,
Mass = Moles * Molar mass = 0.001643 moles * 180.16 g/mol = 0.296 g
c.
1.159 g of sample contains 0.296 g of acetylsalicylic acid
1.213 g of sample contains
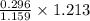 g of acetylsalicylic acid
g of acetylsalicylic acid
Mass of acetylsalicylic acid = 0.3098 g = 309.8 mg
d. Sample contains = 309.8 mg
Manufacturer claiming = 315 mg to 335 mg
Thus , it is not acceptable.