Answer:
0.28 M
Step-by-step explanation:
Concentration of [COF₂] = 2.00 M
Considering the ICE table for the equilibrium as:
2COF₂ (g) ⇔ CO₂ (g) + CF₄ (g)
t = o 2.00
t = eq -2x x x
--------------------------------------------- --------------------------
Moles at eq: 2.00-2x x x
The expression for the equilibrium constant is:
![K_c=\frac {[CO_2][CF_4]}{[COF_2]^2}=8.80](https://img.qammunity.org/2020/formulas/chemistry/college/zt49w9b1p07x9e0aplz1dy6hoi92f6vv1g.png)
So,
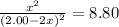
Solving for x, we get that
x = 0.86 M
Equilibrium concentrations :
[CO₂] = [CF₄] = 0.86 M
[COF₂] = 2.00 - 2*0.86 = 0.28 M