Answer:
The number 0 is excluded from the domain of f(x) because f(x) is a rational function which is not defined if the denominator is zero.
Explanation:
The Rational Function is defined as:
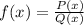 with Q(x) ≠ 0
with Q(x) ≠ 0
Because a rational function is not defined when the denominator is zero.
In this case, Q(x) (the denomitador of the given function) is x. Therefore the domain of the given function is given by all real numbers except the restrictions of the function (where the function is not defined).
f(x) is not defined at x=0, that's why the zero is excluded.