Answer:
8.829 m/s²
Step-by-step explanation:
M = Mass of Earth
m = Mass of Exoplanet
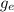 = Acceleration due to gravity on Earth = 9.81 m/s²
= Acceleration due to gravity on Earth = 9.81 m/s²
g = Acceleration due to gravity on Exoplanet
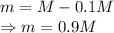
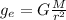
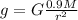
Dividing the equations we get
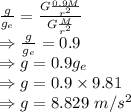
Acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Exoplanet is 8.829 m/s²