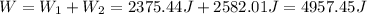Answer:
The total work is 4957.45J
Step-by-step explanation:
For an ideal gas, at constant temperature the definition of work (W) is
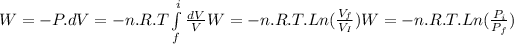
where P is the pressure, V the volume, n the moles number, T the temperature and R the gas constant.
To solve the problem is necessary to replace the two steps in the equation
Stape 1: n = 1 mol, R = 0.082atm.L/K.mol, T = 77ºC = 350K, Pi = 5.50atm and Pf = 2.43atm.
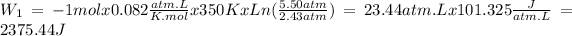
Stape 2: n = 1 mol, R = 0.082atm.L/K.mol, T = 77ºC = 350K, Pi = 2.43atm and Pf = 1.00atm.
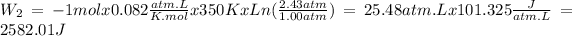
The total work is the sum of the two steps