Answer:
1.88 g of manganese(II) oxide
Step-by-step explanation:
We could exprese the reactions that take place as:
Mn²⁺ (aq) + 2OH⁻ (aq) → Mn(OH)₂ (s)
Mn(OH)₂ → MnO + H₂O
The important aspect is that the ratio of Mn²⁺ to Mn(OH)₂ and then to MnO remains as 1.
- Now we can calculate the starting moles of Mn²⁺ with the concentration (0.491 M) and the volume (54.0 mL = 0.054 L)
0.491 M * 0.054 L =0.026514 mol Mn²⁺
Then we calculate the moles of MnO and finally its mass, using its molecular weight:
0.026514 mol Mn²⁺ *
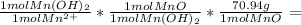 1.88 g MnO
1.88 g MnO