Step-by-step explanation:
Upon dissolution of KCl heat is generated and temperature of the solution raises.
Therefore, heat generated by dissolving 0.25 moles of KCl will be as follows.
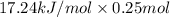
= 4.31 kJ
or, = 4310 J (as 1 kJ = 1000 J)
Mass of solution will be the sum of mass of water and mass of KCl.
Mass of Solution = mass of water + (no. of moles of KCl × molar mass)
= 200 g +
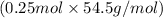
= 200 g + 13.625 g
= 213.625 g
Relation between heat, mass and change in temperature is as follows.
Q =
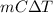
where, C = specific heat of water =
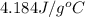
Therefore, putting the given values into the above formula as follows.
Q =
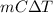
4310 J =
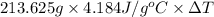
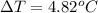
Thus, we can conclude that rise in temperature will be
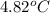 .
.