Answer: The partial pressure of oxygen is 160 mmHg
Step-by-step explanation:
We are given:
Percent of oxygen in air = 21 %
Mole fraction of oxygen in air =
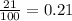
To calculate the partial pressure of oxygen, we use the equation given by Raoult's law, which is:
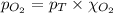
where,
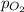 = partial pressure of oxygen = ?
= partial pressure of oxygen = ?
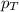 = total pressure of air = 760 mmHg
= total pressure of air = 760 mmHg
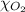 = mole fraction of oxygen = 0.21
= mole fraction of oxygen = 0.21
Putting values in above equation, we get:
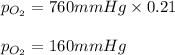
Hence, the partial pressure of oxygen is 160 mmHg