Answer: The chemical equations are written below.
Step-by-step explanation:
For a: Methane reacts with oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide and water.
Combustion reaction is defined as the reaction in which a hydrocarbon reacts with oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide and water
The chemical equation for the combustion of methane follows:
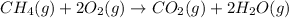
- For b: Butane reacts with oxygen gas to produce carbon dioxide and water.
This is also an example of combustion reaction.
The chemical equation for the combustion of butane follows:
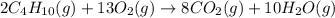
- For c: An aqueous solution of sulfuric acid reacts with aqueous potassium hydroxide to produce potassium sulfate and water.
When an acid reacts with a base, it leads to the formation of salt and water. This reaction is known as neutralization reaction
The chemical equation for the reaction of potassium hydroxide and sulfuric acid follows:
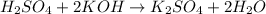
Hence, the chemical equations are written above.