Answer:
(a)-4.15m
(b) 150 Nm
(c) -2.67m
(d)150-6.813149m
Step-by-step explanation:
(a)
The work done by the gravity is
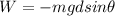 where m is mass, g is gravitational constant,
where m is mass, g is gravitational constant,
 is angle of inclination, F is force on the inclined plane and d is the displacement of the body in the plane.
is angle of inclination, F is force on the inclined plane and d is the displacement of the body in the plane.
W=-(m*9.81*1*sin 25)= -4.1458851m
w--4.15m
Note that m here is mass, not units
(b)
The work done by the applied force is Wa = F *d=150*1=150 Nm
(c)
The work done by the frictional force is
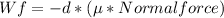
But the normal force is
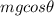
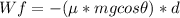 =-(0.3m*9.81*cos25)= -2.6672638m
=-(0.3m*9.81*cos25)= -2.6672638m
Wf=-2.67m
Where m is not units but mass
(d)
The net force is
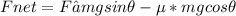
The work done by the net force is
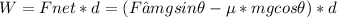
W=(150-4.1458851m-2.6672638m)=150-6.813149m