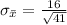Answer:
n = 41
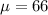
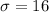
According to the central limit theorem
Let
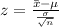 is a standard normal variable
is a standard normal variable
(a) What must be true regarding the distribution of the population in order to use the normal model to compute probabilities regarding the sample mean?
Ans. The population must be normally distributed
b) Assuming the normal model can be used, describe the sampling distribution x over bar.
Approximately normal with
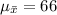 and
and