Answer:
The probability that a healthy person has a temperature above 98.9 Fahrenheit degrees is about P(x>98.9) = 0.1292 or 12.92%.
Explanation:
This is a question of finding the probability of a normally distributed variable, and for this, we have to know that the normal distribution is determined by two parameters: the population mean and the population standard deviation. In this case, they are, respectively,
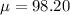 Fahrenheit degrees and
Fahrenheit degrees and
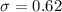 Fahrenheit degrees.
Fahrenheit degrees.
To find probabilities, we can "transform" these "raw" scores into z-scores, or standardized values, using the z-score formula. After this, we can consult the cumulative standard normal table (available in Statistics books or on the Internet) using this z-score (e.g., z = a), for which we have the corresponding cumulative probability, that is, P(z<a). Of course, we can also use statistical software, or even a spreadsheet, to find such probabilities.
A z-score tells us the distance from the mean in standard deviations units for the standardized value of the raw score. A positive value indicates that the value is above the mean. Conversely, a negative value tells us that the value is below the mean.
The formula for this z-score is as follows
z =
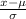 [1]
[1]
Where x is the raw score (x = 98.9 Fahrenheit degrees, in this case).
With this information at hand, we can solve the question.
The probability that a healthy person has a temperature above 98.9 Fahrenheit degrees
We need to find P(x>98.9).
Using formula [1], the z-score for x = 98.9 is
z =
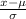
z =
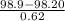
z =
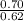
z =
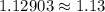
With this value for z (z = 1.13), we can consult the cumulative standard normal table to find the probability for z = 1.13 or P(z<1.13), for which we have a value of P(z<1.13) = 0.8708.
However, we are asked for P(x>98.9) = P(z>1.13), which is the complement probability for P(z<1.13) or
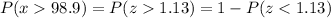
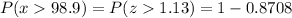
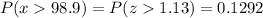
Remember that z is the standardized value for x, so P(x>98.9) = P(z>1.13).
Therefore, the probability that a healthy person has a temperature above 98.9 Fahrenheit degrees is about
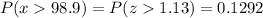 or 12.92%.
or 12.92%.
We can see this area in the graph below.