Answer: The moles of bromine gas at equilibrium is 0.324 moles.
Step-by-step explanation:
To calculate the molarity of solution, we use the equation:
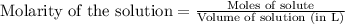 .......(1)
.......(1)
Calculating the initial moles of hydrogen and bromine gas:
Moles of hydrogen gas = 0.682 mol
Volume of solution = 2.00 L
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
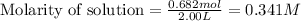
Moles of bromine gas = 0.440 mol
Volume of solution = 2.00 L
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
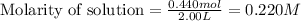
Now, calculating the molarity of hydrogen gas at equilibrium by using equation 1:
Equilibrium moles of hydrogen gas = 0.566 mol
Volume of solution = 2.00 L
Putting values in equation 1, we get:
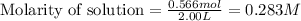
Change in concentration of hydrogen gas = 0.341 - 0.283 = 0.058 M
This change will be same for bromine gas.
Equilibrium concentration of bromine gas =
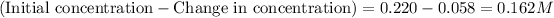
Now, calculating the moles of bromine gas at equilibrium by using equation 1:
Molarity of bromine gas = 0.162 M
Volume of solution = 2.00 L
Putting values in equation 1, we get:

Hence, the moles of bromine gas at equilibrium is 0.324 moles.