Answer:
Let's start by considering the ideal gas law:
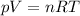
where
p is the gas pressure
V is its volume
n is the number of moles
R is the gas constant
T is the absolute temperature
This equation can also be rewritten as
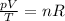
Now, if we consider a fixed amount of gas, this means that the number of moles (n) is constant. So we can rewrite the equation as
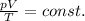
And therefore, if we consider a gas undergoing a certain transformation from 1 to 2, we can write

where 1 indicates the conditions of the gas at the beginning and 2 the conditions of the gas after the process. So, the change in pressure/temperature/volume of the gas can be found by using this equation.